| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Anterior: The front of a
structure. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Arthritis: An inflammation of the
joints. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Arthroscopy: Examination of the
interior of a joint using a microscope-like device that
can be put through a small cut. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Cardiovascular: Referring to the heart
and blood vessels. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Cartilage: A tissue that connects
and supports. Found in the joints, the chest and stiff
tubes, such as voicebox, windpipe, nose and ear. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
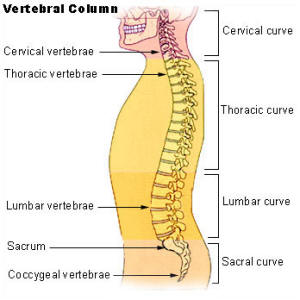 Cervical
Vertebrae: The first seven segments
of the spine, starting from the top of the spinal
column. Cervical
Vertebrae: The first seven segments
of the spine, starting from the top of the spinal
column. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Cervical
Vertebrae: The first seven segments
of the spine, starting from the top of the spinal
column. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Coccygodynia: Pain in the coccyx,
which is also known as the tailbone. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Coccyx: The small bone at the
base of the spinal column. Also known as the tailbone. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Compression
fracture: A spinal fracture that
results from compression of the vertebra. Compression
fractures can occur in any region of the spine. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Congenital: Present at birth. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Disc: The cartilage between
the vertebrae, or backbones. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Dura mater: A membrane that covers
the brain and the spinal cord. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
EMG
(electromyography): A test that measures
muscle response to nerve stimulation. Used to evaluate
muscle weakness. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Epidural: Situated within the
spinal canal, on or over the dura mater. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Fracture: An injury to the bone in
which the tissue of the bone is broken. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Habitus:
A person's looks or
physique. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Headache: A pain in the head. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Herniated
disc: A break in the cartilage
surrounding a disc in the spine, releasing the substance
that cushions the back bones. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Injection: Forcing a liquid, such
as a dose of medicine, into the body using a syringe. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Kyphosis:
A posterior (backward)
curvature of the thoracic spine usually the result of a
disease or a congenital problem. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Laminectomy: A surgical procedure
that is designed to relieve pressure on the spinal cord
or nerve root that is being caused by a slipped or
herniated disk in the lumbar spine. This procedure is
also used in the treatment of spinal stenosis. This
procedure includes removal of a portion of the bone
comprising a vertebra. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Lateral: To the side. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Lumbar
vertebrae: Located on the spinal
column below the thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae
are larger and heavier that those that are higher in the
spinal column because they must support more weight. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
MRI (Magnetic
Resonance Imaging)" A special imaging
technique used to image internal structures of the body,
particularly the soft tissues. An MRI image is often
superior to a normal X-ray image. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Osteoporosis: A reduction in the
amount of bone mass, leading to fractures after minimal
trauma. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Physical
therapy: The use of exercise and
physical activities to condition muscles and improve
level of activity. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Quadriplegia: Total paralysis from the
neck down. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Sacrum: The triangular bone at
the top part of the pelvis. It looks like a wedge set
between the two hip bones. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Sciatica: Inflammation of the
sciatic nerve, usually with pain along the thigh and
leg. Can lead to wasting of the muscles of the lower
leg. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Sciatic nerve: Nerve that stretches
through the thigh, leg and foot. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Scoliosis: A congenital lateral
curvature of the spine. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Spasm: A sudden, involuntary
muscular contraction. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Spinal canal: The canal formed by the
openings in the vertebra through which the spinal cord
and its membranes pass. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Spinal column: The vertebrae that form
the supporting axis of the body. The backbone. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Spinal cord: The part of the nervous
system that is contained in the spinal canal. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Spinal fusion: The joining of an
unstable part of the spine. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Spinal
metastases: Cancer that started from
cancer cells from another part of the body and spread to
the spine. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Spinal
stenosis: An abnormal narrowing of
the spinal canal that may be either congenital or
acquired. Treatment is generally surgical to widen the
spinal canal. Laminectomy may be the indicated surgical
procedure to reduce pressure on the spinal cord. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Syringe: A device for withdrawing
or injecting fluids. A syringe can be used to take a
blood sample or give a dose of medicine. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Thoracic
vertebrae: The 12 segments of the
spinal column of the upper back, located below the
cervical vertebrae and above the lumbar vertebrae on the
spinal column. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Vertebra: One of 23 bones
(excluding the sacrum) in the cervical, thoracic and
lumbar regions that comprise the spine. There are 7
cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae and 5 lumbar
vertebrae. The bottom of the spine is fused and forms
the sacrum. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Vertebral
bodies: Of or pertaining to a
vertebra. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
X-ray: A type of irradiation
used for imaging purposes that uses energy beams of very
short wavelengths that can penetrate most substances
except heavy metals. This is the commonest form of
imaging technique used in clinical practice everywhere
in the world with the image captured on photographic
film. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
